In the 5thC a crack commando unit was sent to purgatory by St Patrick for a crime they didn’t commit. These men promptly escaped from a maximum security stockade into the Gaeltacht underground. Today, still wanted by the church, they survive as soldiers of fortune. If you have a problem – if no one else can help – and if you can find them – maybe you can hire: The F-Team…
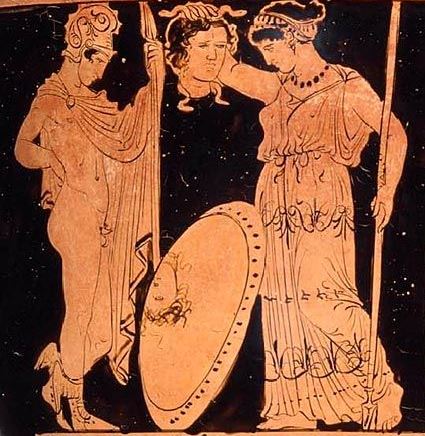
The idea of a group of heroes who battle the monstrous, the fateful and the chaotic at the boundaries of safe everyday existence is a pervasive feature of European mythology, extending back for as long as stories have been recorded. In the Gaelic language zones, perhaps the most important representatives of this legendary theme are Fionn mac Cumhaill and his Fianna.Through their battles (and romantic encounters) with the magical denizens of legend, and their willingness to lay down their lives and suffer to do this, they become heroes who benefit the people, and their stories are marked by an enduring fondness.
What struck me as interesting about the aforementioned story of Aleisoun Pearsoun (put to death for witchcraft in Fife in 1588) was that her ‘story’ of how she acquired her powers seems to mirror and include aspects of that of the legendary Fianna:
1. She – like Fionn – joins a fairy band who take her on a wild adventure.
2. She ‘marries’ (has a sexual initiation) with a fairy she meets in the wilds. Fionn’s paramour was a woman in the form of a deer who he catches when hunting. Their magical son (poetry) is Oisin (‘Little Deer’).
3. She is tested with great adversity by the Otherworld denizens, who make her ill, but is given magical weapons with which to combat them.
4. She overcomes and returns with knowledge of its secrets, and becomes a warrior against the perils of the Otherworld (disease).
In fact, hers is not a dissimilar story to that of traditional Gaelic folk-healer characters such as Biddy Early (Ireland 19thC) and elsewhere besides. It is a feature pertinent to stories of ‘shamans’ and ‘medicine men’ etc from around the pre-modernised world.
The Fianna and the Sluagh Sidhe:
The fact that the ‘wild band’ or ‘fairy cavalcade’ in Gaelic folk-belief would have had something to do with Fionn and the Fianna often seems implicit, but it is quite rare to see this connection made explicitly in pre-20thC folklore accounts. Aleisoun Pearsoun’s fairy-band were apparently capable of both mirth and malice, which is a possibly a fair description of the legendary antics of the warlike Fianna. Nonetheless, apart from her kindred spirits who protect her, the cavalcade seem mostly harmful, and it is in understanding how to deal with this harm that she understands how to cure diseases. For this reason, we must turn our attention to the chaotic harmful fairy cavalcade, referred to in folklore as the Sluagh Sidhe or Sluagh Sith/Slieu Shee.
‘Sluagh Sidhe’ translates literally as ‘Fairy Host’ or ‘Fairy Army’. Robert Kirk (c.1690) provided one of the earliest accounts of the belief in these fairy hosts:
“… Moreover, this Life of ours being called a Warfair, and God’s saying that at last there will be no Peace to the Wicked, our bussie and silent Companions also being called Siths, or People at Rest and Quiet, in respect of us; and withall many Ghosts appearing to Men that want this Second Sight, in the very Shapes, and speaking the same Language, they did when incorporate and alive with us; a Matter that is of ane old imprescriptible Tradition, (our Highlanders making still a Distinction betwixt Sluagh Saoghalta and Sluagh Sith, averring that the Souls goe to the Sith when dislodged;)… “
As can be seen, Kirk gave two forms supernatural ‘Sluagh’, An Sluagh Saoghalta meaning, literally, ‘The Temporal/Earthly Host’. Kirk himself offers no translation to explain what he calls ‘Sluagh Saoghalta’ (‘Slooa Sheelta’) and uses the term only once. The implication from his fairy narrative is that one host is ‘spiritual’ and the other ‘of the mundane world’, probably meaning those ‘left behind’ due to sinfulness during their lives and more prone to the brutish acts that characterised a difficult existence. So far as I have been able to find out, there are few other references to ‘Sluagh Saoghalta’ from recorded folklore, it being more of a term used in Gaelic christian literature, so let us focus on the Sluagh Sidhe/Sith, a term which probably encompasses both ideas:
Source: Popular tales of the West Highlands, orally collected, Vol. 3 – John Francis Campbell, Pub: Edmonston and Douglas, 1862; pp.340-341
“….A doctor told this anecdote—
“Do you see that kind of shoulder on the hill? Well, a man told me that he was walking along there with another who used to “go with the fairies,” and he said to him—
“‘ I know that they are coming for me this night. If they come, I must go with them; and I shall see them come, and the first that come will make a bow to me, and pass on; and so I shall know that they are going to take me with them.’
“‘Well,’ said the man, ‘we had not gone far when the man called out, ‘Tha iad so air tighin.’ These are come. I see a number of ‘ sluagh’ the people; and now they are making bows to me. And now they are gone.’ And then he was quiet for a while. Then he began again; and at last he began to cry out to hold him, or that he would be off.
“Well,” said the doctor, “the man was a bold fellow, and he held on by the other, and he began to run, and leap, and at last (as the man told me) he was fairly lifted up by the ‘sluagh,’ and taken away from him, and he found him about a couple of miles further on, laid on the ground. He told him that they had carried him through the air, and dropped him there. And,” said the doctor, “that is a story that was told me as a fact, a very short time ago, by the man whom I was attending.”
Not far off I was told this in a house full of people, all of whom knew the story, and seemed to believe it implicitly.”
This account was corroborated by Alexander Carmichael (Carmina Gaedelica Volume 2, pp.3301-331) – as usual, my emphases:
Sluagh – ‘Hosts’, the spirit world – the ‘hosts’ are the spirits of mortals who have died. The people have many curious stories on this subject. According to one informant, the spirits fly about “n’an sgrioslaich mhor, a sios agusa suas air uachdar an domhain mar na truidean’ – ‘In great clouds, up and down the face of the world like the starlings, and come back to the scenes of their earthly transgressions’. No soul of them is without the clouds of earth, dimming the brightness of the works of God, nor can any make heaven until satisfaction is made for the sins on earth. In bad nights, the hosts shelter themselves, ‘ fo gath chuiseaga bheaga ruadha agus bhua-ghallan bheaga bhuidhe’ – ‘behind little russet docken stems and little yellow ragwort stalks’. They fight battles in the air as men do on the earth. They may be heard and seen on clear frosty nights, advancing and retreating, retreating and advancing, against one another. After a battle, as I was told in Barra, their crimson blood may be seen staining rocks and stones. ‘Fuil nan sluagh’, the blood of the hosts is the beautiful red ‘crotal’ of the rocks, melted by frost.
These spirits used to kill cats and dogs, sheep and cattle, with their unerring venemous darts. They commanded men to follow them, and men obeyed, having no alternative.
It was these men of earth who slew and maimed at the bidding of their spirit-masters, who in return ill-treated them in a most pitiless manner. ‘Bhiodh iad ’gan loireadh agus ’gan loineadh agus ’gan luidreadh anus gach lod, lud agus lon’–They would be rolling and dragging and trouncing them in mud and mire and pools. ‘There is less faith now, and people see less, for seeing is of faith. God grant to thee and to me, my dear, the faith of the great Son of the lovely Mary.’ This is the substance of a graphic account of the ‘sluagh,’ given me in Uist by a bright old woman, endowed with many natural gifts and possessed of much old lore. There are men to whom the spirits are partial, and who have been carried off by them more than once. A man in Benbecula was taken up several times. His friends assured me that night became a terror to this man, and that ultimately he would on no account cross the threshold after dusk. He died, they said, from the extreme exhaustion consequent on these excursions. When the spirits flew past his house, the man would wince as if undergoing a great mental struggle, and fighting against forces unseen of those around him. A man in Lismore suffered under precisely similar conditions. More than once he disappeared mysteriously from the midst of his companions, and as mysteriously reappeared utterly exhausted and prostrate. He was under vows not to reveal what had occurred on these aerial travels.
I took down several stories of persons who went with the ‘hosts.’ Here is one of the stories of the ‘hosts’ summarised:–The beautiful daughter of a king of France was taken up by the ‘hosts,’ and carried about in the air, over lands and seas, continents and islands, till they came to the little island of Heistamal, behind Creagorry, in Benbecula, where they laid her down in such an injured state that she died from the hard treatment; not, however, till she had told about the lands to which she had been carried, and of the great hardships she had endured while travelling through space. The people of the island buried the princess where she was found.
The ‘sluagh’ are supposed to come from the west; and therefore, when a person is dying, the door and the windows on the west side of the house are secured to keep out the malicious spirits. In Ross-shire, the door and windows of a house in which a person is dying are opened, in order that the liberated soul may escape to heaven. In Killtarlity, when children are being brought into the world, locks of chests and of doors are opened, this being supposed, according to traditional belief, to facilitate childbirth.
These Hebridean and Highland accounts concur with records of similar beliefs from Ireland and the Isle of Man. The Sluagh Sidhe were dangerous, vengeful and often angry – they were represented (as Aleisoun Pearsoun was informed) by gusts of wind which marked their passing. These fairy ‘blasts’ might burn your skin with ignis sacer or boils or other visible cutaneous conditions. They strike you with fairy darts rendering you sick, or paralysed down one side (a ‘stroke’, the name still used in medicine today). They might also carry you away in a state of delirium to a place you had no intention of being – you would be ‘taken‘ by them, sometimes into their own fairy world!
The Sluagh Sidhe/Sith were – like the Fianna of ancient Ireland – bands of souls who roamed the world outside of the laws of settled everyday life. They were dangerous and liminal, yet potentially helpful and – in the fairy faith discussed by Kirk and other commentators – could redeem themselves, sometimes by sharing the knowledge of how to ‘heal’ the harm they cause, and from there could pass to a different place – in the west, beyond the sunset.
A Fairy Doctor was a specialist who understood these modes of harm caused by these Fairy Hosts. He or she also understood the ‘principle of inversion’ which governed how we and the otherworld interacted together, and was able to intervene or advise in redressing this balance.